Lens Equation
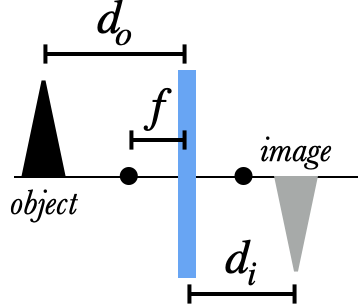
When a lens or mirror creates an image from an object, we define the following distances:
- $f$ is the focal length of the device
- $d_o$ is the distance from the object to the device
- $d_i$ is the distance from the image to the device
These three distances are related by the lens equation:
Since we are normally interested in finding the image distance, this can be rewritten as $$d_i={d_of\over d_o-f}$$
The object distance $d_o$ is always positive, but the image distance $d_i$ can sometimes be negative. The sign of $d_i$ tells you what kind of image you have:
If $d_i<0$, the image is virtual.
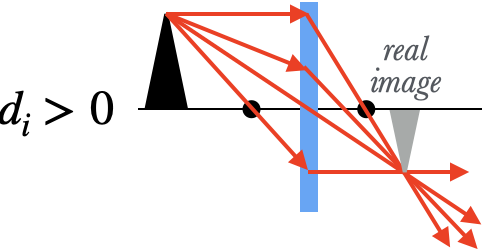
We get a real image when the denominator above, $d_o-f$, is positive, which is true when $d_o>f$. This occurs when the object is outside of the focal point. The rays of light from the object don't diverge as much once they hit the lens, and the lens is able to bend those rays enough so that they converge to a point, and form a real image.
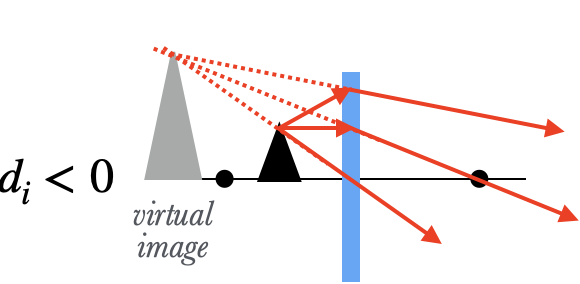
When the object is inside the focal point, on the other hand, the rays of light are diverging too much when they hit the lens, and the lens isn't strong enough to make the rays converge: the best it can do is to make the rays diverge less. An eye which sees these diverging rays on the other side traces them back to a spot behind the lens, and sees a virtual image there.
The side that the image appears on depends on whether you have a lens or a mirror. For a lens, real images appear on the far side of the lens (from the object), and virtual images appear on the near side. For a mirror, real images appear on the near side, while virtual images appear on the far side (just like with a flat mirror ).
